3-Tier Architecture in Data Warehouse: Components and Benefits
-
Pradyumn Singh / 3 days ago
- 15
- 11 min read
Whether you're an aspiring data analyst, business intelligence professional, or a
software engineer, understanding this architecture is crucial. Enrolling in a quality Data
Science Course not only helps you master this fundamental concept but also equips you with the
practical skills to implement and work with data warehouses in real-world scenarios.
In this article, we’ll explore the components of the 3-tier architecture, how
they interact, and the numerous benefits it offers to modern enterprises.
What is a Data Warehouse?
A data warehouse is a centralized repository where data from multiple sources is
stored. It is designed specifically for querying and analysis, not transaction processing.
Unlike operational databases, which focus on CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations, a
data warehouse focuses on analytics, reporting, and decision-making processes.
Data in a warehouse is typically cleaned, transformed, and organized to allow for
fast and reliable business intelligence. It's the backbone of data-driven decision-making in
sectors like finance, healthcare, retail, and marketing.
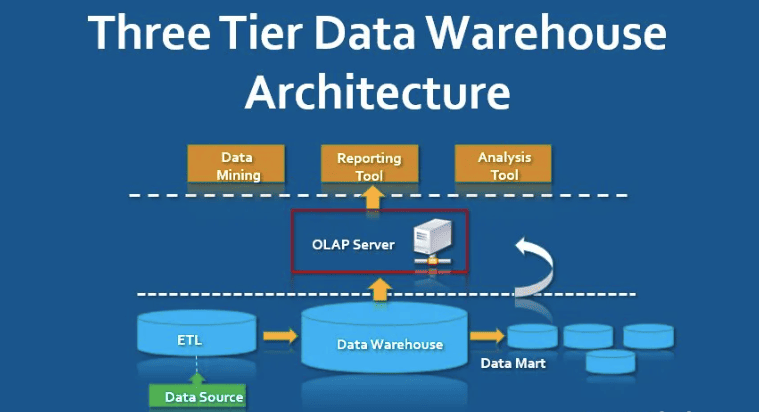
What is the 3-Tier Architecture of Data Warehouse?
The 3-tier architecture of a data warehouse is a layered structure designed to
improve efficiency, scalability, and maintainability of data storage and analysis. It divides
the data warehousing system into three levels:
- Bottom Tier – Data Source Layer
- Middle Tier – Data Storage and Processing Layer
- Top Tier – Front-End and Presentation Layer
1. Bottom Tier: Data Source Layer
The bottom tier is responsible for gathering and integrating data from various
sources such as relational databases (e.g., MySQL, Oracle), flat files (e.g., CSVs), NoSQL
systems, ERP systems, CRM tools, social media platforms, and more. This layer primarily deals
with ETL processes:
- Extract: Pulling data from multiple, disparate sources.
- Transform: Cleaning, reformatting, deduplicating, and
enriching the data to match the warehouse schema.
- Load: Inserting the transformed data into the data
warehouse storage system.
Modern ETL tools like Talend, Apache NiFi, and Informatica make this process more
automated and efficient. In cloud environments, tools like AWS Glue or Google Cloud Dataflow are
frequently used. A Data Science Course often includes modules on data ingestion and
transformation, equipping learners with essential skills in handling this foundational layer.
2. Middle Tier: Data Storage and Processing Layer
This is the core of the data warehouse. Once the data is extracted and cleaned,
it lands in this middle layer where it's stored in a structured format optimized for analytical
queries. There are two major components in this tier:
a) Data Warehouse Storage
This is where the processed data is stored. Unlike operational databases, which
are normalized for transactional integrity, data warehouses often use denormalized or
star/snowflake schemas for faster querying.
- Traditional: Oracle Warehouse, Teradata, IBM Db2
- Cloud-Based: Amazon Redshift, Google BigQuery, Snowflake
b) OLAP Servers
Online Analytical Processing (OLAP) servers help perform complex analytical
queries quickly and efficiently. They support operations like slicing, dicing, roll-up, and
drill-down across multiple dimensions.
- MOLAP (Multidimensional OLAP): Uses precomputed
multidimensional cubes for fast performance.
- ROLAP (Relational OLAP): Uses relational databases and
generates queries on the fly.
This tier ensures that decision-makers can derive meaningful insights from the
data with minimal latency. A Data Science Course helps students understand schema design, OLAP
concepts, and query optimization techniques relevant to this layer.
3. Top Tier: Front-End and Presentation Layer
This is the user-facing layer of the architecture. It provides access to data for
analysis and visualization through dashboards, reports, and analytical tools.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools: Such as Tableau, Power
BI, QlikView, or Looker.
- Custom Dashboards: Designed for specific stakeholders
like marketing, finance, or operations.
- Ad-hoc Querying Interfaces: Enabling users to write SQL
or drag-and-drop queries to explore data.
- APIs: Allowing integration with other apps or platforms.
Users can make strategic decisions based on charts, graphs, and KPIs generated
from the warehouse data. Modern Data Science Courses often include hands-on labs with BI tools
and help students build their own dashboards from scratch.
Benefits of the 3-Tier Architecture of Data Warehouse
- 1. Separation of Concerns: By dividing the system into
three distinct layers, each component can be developed, scaled, and maintained
independently. This modularity enhances the system’s flexibility and maintainability.
- 2. Scalability: As data volumes grow, each tier can be
scaled independently. For example, you can upgrade your storage solution without affecting
the user interface or data ingestion pipelines.
- 3. Enhanced Security: Each tier can implement its own
set of access controls and encryption, minimizing the risk of unauthorized access or data
leaks.
- 4. Improved Performance: Data is pre-processed and
optimized in the middle tier, leading to faster query response times and better performance
for end-users.
- 5. Robust Data Governance: Centralized data storage with
auditing, lineage tracking, and version control makes compliance with data regulations
easier.
- 6. Better Decision-Making: With real-time dashboards and
reporting capabilities in the top tier, decision-makers can access insights quickly, leading
to timely and informed actions.
Real-World Applications
- Healthcare: Track patient outcomes, hospital
performance, and supply chain efficiency.
- Retail: Analyze customer behavior, optimize inventory,
and predict sales trends.
- Banking: Monitor fraud detection patterns, risk
assessments, and customer segmentation.
- E-commerce: Power recommendation systems, track customer
journeys, and manage logistics.
Understanding this architecture is not just theoretical, it directly applies to
practical scenarios that data professionals encounter every day. A Data Science Course with a
strong focus on data engineering and warehousing principles is essential for anyone looking to
break into these fields.
Why Learn 3-Tier Data Warehouse Architecture in a Data Science Course?
If you're aspiring to become a data scientist, analyst, or engineer, it’s crucial
to have a thorough understanding of how data is stored, managed, and accessed. A high-quality
Data Science Course will provide:
- Hands-on experience with ETL pipelines
- Schema design and data modeling best practices
- Exposure to OLAP systems and BI tools
- Real-world projects that mirror enterprise data challenges
The goal isn't just to learn theory but to gain the ability to build and optimize
systems that handle real, large-scale data problems.
FAQs on 3-Tier Architecture in Data Warehouse
Q1. What is 3-tier architecture in a data warehouse?
A: It’s
a structure that divides the data warehouse system into three layers: bottom (data), middle
(processing), and top (presentation).
Q2. What are the three tiers?
A:
- Bottom Tier: Data sources and storage (like databases).
- Middle Tier: OLAP servers or processing logic.
- Top Tier: Front-end tools for reporting and data
visualization.
Q3. Why use a 3-tier architecture?
A: It improves data
organization, enhances scalability, and separates processing from presentation for better
performance.
Q4. What happens in the bottom tier?
A: Raw data from
multiple sources is extracted, transformed, and loaded (ETL) into the data warehouse.
Q5. What does the middle tier do?
A: It processes and
organizes data using OLAP or other tools to make it ready for analysis.
Final Thoughts
The 3-tier architecture of data warehouse remains a gold standard in organizing
enterprise data efficiently. It brings structure, performance, and clarity to the complex
process of turning raw data into actionable insights.
As the demand for data professionals continues to grow, gaining expertise in such
architectures is more valuable than ever. A practical and up-to-date Data Science Course can be
your launchpad into this exciting and rewarding field, providing both theoretical knowledge and
hands-on experience with modern data warehousing tools.
So if you're ready to take the next step in your data career, choose a training
program that not only teaches you the basics—but also prepares you