Generative AI vs. Traditional AI: Key Differences, Industry Applications, and Impact
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has changed many industries, making technology smarter and more interactive. Over time, AI has grown from simple automated systems to advanced tools that can learn and adapt on their own. This progress has sparked discussions about the differences between Generative AI and Traditional AI.
Generative AI stands out because it creates new content, such as images, text, music, or videos, that looks and feels human-made. It’s being used in a wide range of fields, including art, writing, healthcare, and even drug discovery.
“Experts predict that Generative AI could boost the global economy by 10%.”
In this article, we’ll break down the key differences between Generative AI and Traditional AI. We’ll also explain how Generative AI works and how it solves the limitations of rule-based systems in simple terms.
What is Traditional AI (TA)?
Traditional AI, also known as rule-based or symbolic AI, operates using predefined rules and logic. It mimics human thinking by analyzing data and solving problems in specific ways. Traditional AI has evolved into key areas, such as:
- Machine Learning (ML): Algorithms that learn from data, used in systems like Netflix or Amazon recommendations.
- Deep Learning (DL): Advanced neural networks that power technologies like self-driving cars and voice assistants.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Helps computers understand human language, used in chatbots and translation apps.
- Computer Vision: Enables computers to interpret images, used in facial recognition and medical image analysis.
Strengths and Limitations of Traditional AI:
Strengths:
- Accuracy and Speed: Good at handling repetitive tasks quickly.
- Data Handling: Can analyze large amounts of data efficiently.
- Scalability: Can be expanded for large operations.
Limitations:
- Limited Creativity: Cannot generate new ideas or think creatively.
- Poor Adaptability: Struggles with new, unfamiliar situations.
- No Context Understanding: Cannot grasp human emotions or complex language nuances.
What is Generative AI (Gen AI)?
Generative AI is a type of AI that creates new content like images, text, music, and videos. Unlike Traditional AI, which follows fixed rules, Generative AI uses machine learning to analyze data, recognize patterns, and generate content that feels human-made. It’s more creative and flexible than Traditional AI, allowing it to produce original outputs.
Applications of Generative AI
Generative AI is used to create new things, not just analyze data. Some common applications include:
- Image Generation: Creating realistic photos or artistic designs.
- Text Generation: Writing content that sounds human-like.
- Music Composition: Composing original music.
- Video Synthesis: Editing or generating new videos.
- Drug Discovery: Identifying new drugs by understanding chemical patterns.
Generative AI Models
Generative AI uses specific models, such as:
- Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs): Two networks work together to create realistic images or videos.
- Variational Autoencoders (VAEs): Compresses and reconstructs data to generate new outputs, like designing new molecules.
Strengths and Limitations of Generative AI:
Strengths:
- Creative Content Creation: Makes content for design, entertainment, and marketing.
- Speed: Works faster than humans in creating content.
- Personalization: Can customize content for individuals, like in ads or learning.
- Natural Communication: Can have conversations that feel human-like.
Limitations:
- Lacks True Originality: It creates unique content but doesn’t come up with groundbreaking ideas.
- Data Dependency: The quality of its work depends on the data it’s trained on.
- Bias Issues: It may create biased or unfair content if the data is biased.
- Ethical Concerns: Generative AI can be misused to create deceptive content like deepfakes.
Generative AI vs. Traditional AI: Key Differences:
1) Problem-Solving Approach:
- Traditional AI (TA): Follows fixed rules to solve problems. It works well for clear, structured tasks but struggles with new or unclear situations.
- Generative AI (Gen AI): Learns from data, recognizes patterns, and can create new solutions or content. It’s more flexible and can handle complex problems.
2) Techniques and Models:
- TA: Uses rule-based systems like decision trees and expert systems to work within set boundaries.
- Gen AI: Uses advanced models like neural networks (GANs and VAEs) to create new content or data that mimics human creativity.
3) Data Requirements:
- TA: Works with smaller, specific datasets and follows predefined rules.
- Gen AI: Needs large, diverse datasets to learn effectively and generate accurate outputs.
4) Strengths:
- TA: Reliable and efficient for repetitive tasks, processing large data quickly.
- Gen AI: Creative and adaptable, able to generate original content and solve complex problems.
5) Limitations:
- TA: Inflexible and cannot handle creative tasks or adapt to new challenges.
- Gen AI: Dependent on high-quality data and can inherit biases. Requires significant computational power.
6) Applications:
- TA: Used in data analysis, customer support chatbots, and process automation.
- Gen AI: Applied in creative fields like art, music, content generation, and innovative problem-solving like drug discovery.
Use Cases of Generative AI vs. Traditional AI:
- Image Synthesis:
- Gen AI: Creates unique images, even if they weren’t in the training data.
- TA: Enhances or edits existing images with rule-based adjustments.
- Chatbots:
- TA: Rule-based chatbots for structured queries (e.g., customer service).
- Gen AI: Dynamic, human-like chatbots that improve over time.
- Language Translation:
- TA: Uses rules for basic translations.
- Gen AI: Understands context for more accurate, nuanced translations.
- Content Generation:
- Gen AI: Generates articles or digital art based on large datasets.
- TA: Follows rules for consistent content generation.
- Recommendation Systems:
- TA: Recommends based on past behavior (e.g., similar items).
- Gen AI: Personalizes recommendations based on user preferences, adapting over time.
- Speech Synthesis:
- Gen AI: Makes voices sound natural and expressive.
- TA: Ensures speech is clear and accurate.
- Medical Diagnosis:
- TA: Diagnoses based on symptoms and structured data.
- Gen AI: Finds patterns in medical data for more accurate predictions.
- Autonomous Vehicles:
- TA: Manages rule-based systems for safety and traffic laws.
- Gen AI: Learned from real-time data to make driving decisions.
- Financial Predictions:
- TA: Predicts market trends using historical data.
- Gen AI: Recognizes complex patterns in market data for deeper insights and predictions.
Future of Generative AI
Generative AI has made huge strides recently, with technologies like OpenAI’s GPT-3 and Nvidia’s StyleGAN breaking new ground. These AI systems are poised to reshape creativity and innovation in the years to come.
As we tap into its potential, it’s essential to ensure that Generative AI is used ethically and responsibly.
In the future, we’ll see more advanced models like GPT-4, Llama 2, and Mistral that can process different types of data like images, language, and sound, making them more dynamic and smarter. Small language models (SLMs) like PHI-2 and Mistral 7B will help push Gen AI applications further by allowing businesses to tailor AI to their specific needs, speeding up its adoption.
Tools like LangChain and LlamaIndex are making it easier to create autonomous agents—AI that can learn, adapt, and make decisions with minimal human input. This will help Gen AI work more effectively in real-time across various industries.
Impact of Generative AI on Various Industries
As Gen AI evolves, it’s transforming industries and reshaping how businesses operate:
Healthcare
Generative AI can greatly impact healthcare by helping doctors predict and prevent diseases. It can analyze large amounts of medical data to find patterns that humans might miss, supporting accurate diagnoses and personalized treatments. It’s also being used to speed up drug discovery by analyzing molecular structures and predicting how drugs might interact.
Gen AI can also help healthcare providers optimize resources, reduce costs, and improve patient care and outcomes.
Finance
In finance, Gen AI enables institutions to better understand market trends and sentiments, leading to more accurate investment predictions and risk management. It can also detect fraud by spotting unusual transaction patterns, making financial systems more secure. Additionally, Gen AI helps personalize services, offering customers financial products tailored to their preferences and needs.
Education
Generative AI is changing the education system by creating more personalized learning experiences for students. It can adapt teaching methods to each student’s needs, improving engagement and academic performance. For teachers, it automates tasks like grading and helps create interactive lessons, saving time and effort.
Digital Art
Generative AI is revolutionizing the world of art by making it easier for anyone to create unique, customized designs. This is transforming industries like fashion, architecture, and interior design, allowing for rapid prototyping and personalized designs that reflect individual tastes.
Entertainment
In entertainment, Gen AI is changing how stories are told. It can create immersive worlds and interactive plots that engage audiences in new ways. Gen AI is also helping with content creation, from writing stories and composing music to generating artwork. Plus, it can personalize user experiences, making recommendations based on individual preferences and interests.
Ethical Considerations of Generative AI
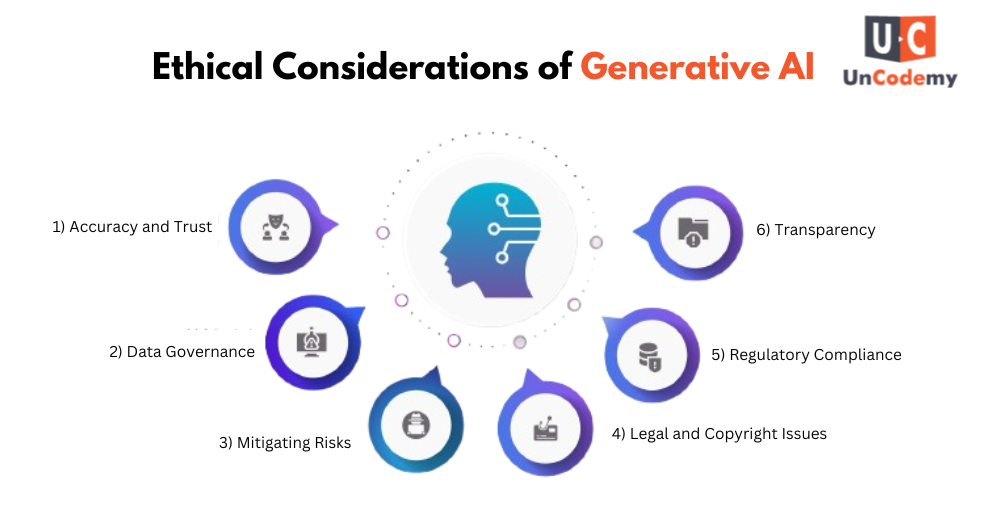
Generative AI brings incredible possibilities, but it also raises important ethical issues that need to be addressed to ensure it’s used responsibly. As Gen AI is expected to create 10% of the total data by 2025, it’s essential to focus on its ethical use.
Here are some key ethical considerations for Gen AI:
1) Accuracy and Trust
Generative AI depends on the data it’s trained on, so if the data is inaccurate or biased, the AI’s decisions and outputs will be too. It’s important to make sure that the data used for training is accurate, fair, and reflects a variety of perspectives. This helps prevent harmful stereotypes and biased decisions.
2) Data Governance
Since Gen AI often uses personal or sensitive data, there are concerns about privacy and security. Organizations must have strong data governance in place to protect this data and comply with regulations like GDPR and CCPA. This ensures that data is handled safely and respectfully.
3) Mitigating Risks
While Gen AI can be powerful, it can also cause harm if it’s not carefully managed. For example, AI might generate incorrect financial data or create misleading images, leading to legal issues or public backlash. To prevent this, it’s important to have systems in place to review AI outputs and clearly define accountability for any risks.
4) Legal and Copyright Issues
Generative AI can create original content, which raises questions about intellectual property. Who owns the content created by AI? There have been legal cases where artists sued AI platforms for using their work without permission. Organizations need to think about how they handle ownership and give proper credit to avoid plagiarism or legal issues.
5) Regulatory Compliance
Governments are starting to regulate the development and use of Gen AI. Businesses must comply with these laws to avoid legal problems and ensure their AI systems are transparent and trustworthy. Following these regulations helps maintain public confidence in AI.
6) Transparency
To build trust, it’s important to be transparent about how Gen AI works. Users should understand how decisions are made by AI and be aware of any biases or limitations it might have. This is becoming increasingly important as AI is used more widely.
7) Deepfakes
Gen AI’s ability to create realistic videos and audio has led to the rise of deepfakes—manipulated media that can cause serious problems, from spreading misinformation to damaging reputations. As these technologies evolve, creators must be responsible and ensure that their content is truthful and not misleading.
8) Bias
Gen AI can inherit biases from the data it’s trained on. This is particularly concerning in areas like hiring or lending, where biased decisions can have real-world consequences. Companies must actively work to identify and eliminate any biases in their AI systems to ensure fair outcomes for everyone.
9) Job Displacement
As Gen AI automates more tasks, it may lead to job loss in certain industries. This raises ethical concerns about the impact on workers and the economy. Companies should think about ways to retrain and reskill employees whose jobs might be automated, helping them transition to new roles. At the same time, the rise of AI will create new job opportunities in fields like AI development job, data science, machine learning engineering, and AI ethics. By focusing on upskilling workers for these emerging roles, companies can help balance the economic shift caused by automation.
Understanding Emerging Trends in AI
AI is evolving quickly, and new trends are emerging that are expanding the capabilities of Generative AI. These trends show how AI can change industries and impact the global economy.
1) Explainable AI (XAI)
AI systems can sometimes be a “black box,” meaning we can see the results but not fully understand how the AI made its decisions. Explainable AI (XAI) aims to make these systems more transparent. With XAI, we can explain why AI makes certain choices, making the process more understandable to humans.
This transparency builds trust in AI and helps address ethical concerns. For this to work well, AI systems will need to interact with human knowledge and experience, requiring new ways to combine AI and human decision-making.
2) Neurosymbolic AI
Neurosymbolic AI is an approach that blends two different types of AI: neural networks and symbolic reasoning. Neural networks are great at recognizing patterns (like identifying objects in images), while symbolic reasoning is better at handling tasks like planning, problem-solving, and decision-making.
By combining these strengths, neurosymbolic AI aims to create smarter systems that can reason and think more like humans. This approach makes AI more effective in tasks that require both pattern recognition and logical thinking.
Conclusion
Generative AI is poised to transform creativity and innovation in the years ahead. Its ability to revolutionize industries, boost creativity, and address complex challenges is enormous. By recognizing both its potential and the challenges it presents, we can better prepare to use its capabilities for the greater good. Through responsible innovation and ethical practices, we can unlock the full power of AI for a positive impact.
FAQs: –
- What is the key difference between Generative AI and Traditional AI?
Ans. Generative AI creates new content based on patterns it learns from data, whereas Traditional AI relies on predefined rules and algorithms to perform specific tasks. Gen AI is more flexible and creative, while Traditional AI excels in tasks with clear instructions. - How does Generative AI handle creative tasks?
Ans. Generative AI can produce original content like text, images, music, and videos by analyzing existing data. It mimics human creativity and is capable of creating content that may not exist yet, offering immense potential for art, design, and entertainment. - Can Generative AI improve industries like healthcare and finance?
Ans. Yes, Generative AI can revolutionize industries such as healthcare by aiding in disease prediction, personalized treatments, and drug discovery. In finance, it helps analyze market trends, improve risk management, and detect fraudulent activities. - What ethical challenges should be considered when using Generative AI?
Ans. Key ethical issues include accuracy, data governance, transparency, and avoiding biases. Gen AI can also create misleading content, like deepfakes, which raises concerns about its potential for misinformation or malicious use. - How will Generative AI impact jobs?
Ans. Generative AI may automate tasks like data entry and customer service, affecting jobs with repetitive duties. However, roles that require creativity, emotional intelligence, or critical thinking, such as teaching or management, are less likely to be replaced.